Node Overview
A node is a computer running an instance of Quai that communicates (peers) with other nodes. The web of communication between nodes makes up Quai Network.
Nodes are responsible for validating and propagating transactions across Quai Network. Each node maintains a copy of all or a subset of chains within the network, and handles the computation of state changes when a new block is added to their local copy of the ledger. Nodes uphold the integrity of Quai by ensuring the validity and accurate recording of all transactions.
There are 4 unique kinds of nodes that exist within Quai Network that manage different subsets of data, serve different purposes, and have differing hardware requirements.
If you're ready to start setting up your node now, check out the written tutorial in the Quai docs, or the video tutorial on the Quai YouTube.
Node Types
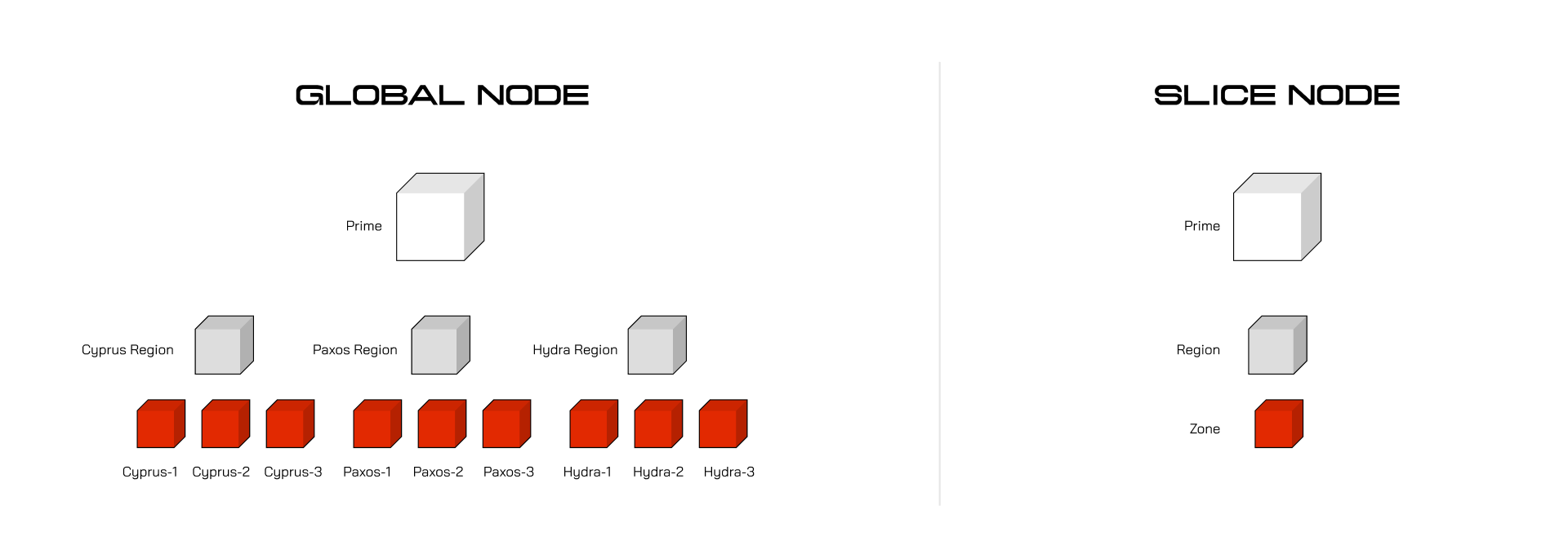
Global Node
A global node on Quai Network maintains the ledger and generates proposed blocks for mining in all shards. Global nodes operate by sending and receiving the latest blocks along with their header data to its peers in the network. Global nodes also have the ability to serve requests that query each of the shards through WebSockets and HTTP. Currently, global nodes on Quai Network serve as archive nodes since historical state is not pruned.
The hardware requirement to run a global node when Quai is at low/no load:
- Fast CPU with 8+ cores
- 32GB+ RAM
- Fast SSD with at least 3TB free space
- 10+ MBit/sec download Internet service
The hardware requirement to run a global node when Quai is at high/maximum load:
- Fast CPU with 16+ cores
- 64GB+ RAM
- Fast SSD with at least 3TB free space
- 10+ MBit/sec download Internet service
Slice Node
A slice node on the network is a subset of a global node that validates prime, a single region, and a single zone. An example of a slice node would be the combination of prime, Cyprus, and Cyprus1. The benefit to running a slice node is that a node needs fewer resources. The trade-off is that cross-node validation is delegated to the peered global nodes or coordinate slices. A slice node is the smallest subset of the network that a node can run and still trustlessly access the network.
The hardware requirement to run a slice node when Quai is at low/no load:
- CPU with 4+ cores
- 16GB+ RAM
- Fast SSD with at least 1TB free space
- 10+ MBit/sec download Internet service
The hardware requirement to run a slice node when Quai is at high/maximum load:
- CPU with 8+ cores
- 24GB+ RAM
- Fast SSD with at least 1TB free space
- 10+ MBit/sec download Internet service
Multi-Slice Node
A multi-slice node is a node that is also running one or more additional region or zone chains coordinate to the selected slice. Multi-slice nodes can be beneficial to node operators because it allows them to identify coordinate chain contention more quickly, lowering their uncle rate.
Multi-slice nodes are not currently a pre-set configuration, however advanced node operators can explore this construction.
Watcher Node
Watcher nodes are Quai Network nodes that observe a single subordinate Quai blockchain. Watcher nodes can be useful for organizations and businesses that are primarily monitoring a single Quai Network context, and are not concerned with coordinate or dominant chains. Watcher nodes are not a trustless way to interact with Quai Network, as they trust in the benevolence of dominant contexts.
Watcher nodes are not currently a pre-set configuration.
Networking and Conventions
| Chain Name | Chain Index | Peering Port (TCP/UDP) |
|---|---|---|
| Prime | 30303 | |
| Cyprus | 30304 | |
| Paxos | 30305 | |
| Hydra | 30306 | |
| Cyprus-1 | [0 0] | 30307 |
| Cyprus-2 | [0 1] | 30308 |
| Cyprus-3 | [0 2] | 30309 |
| Paxos-1 | [1 0] | 30310 |
| Paxos-2 | [1 1] | 30311 |
| Paxos-3 | [1 2] | 30312 |
| Hydra-1 | [2 0] | 30313 |
| Hydra-2 | [2 1] | 30314 |
| Hydra-3 | [2 2] | 30315 |